Control the Rate of Reactions and Regulate Cell Processes
Catalysts slow down the rates of chemical reactions b. To regulate the rate of chemical reactions in various cells.
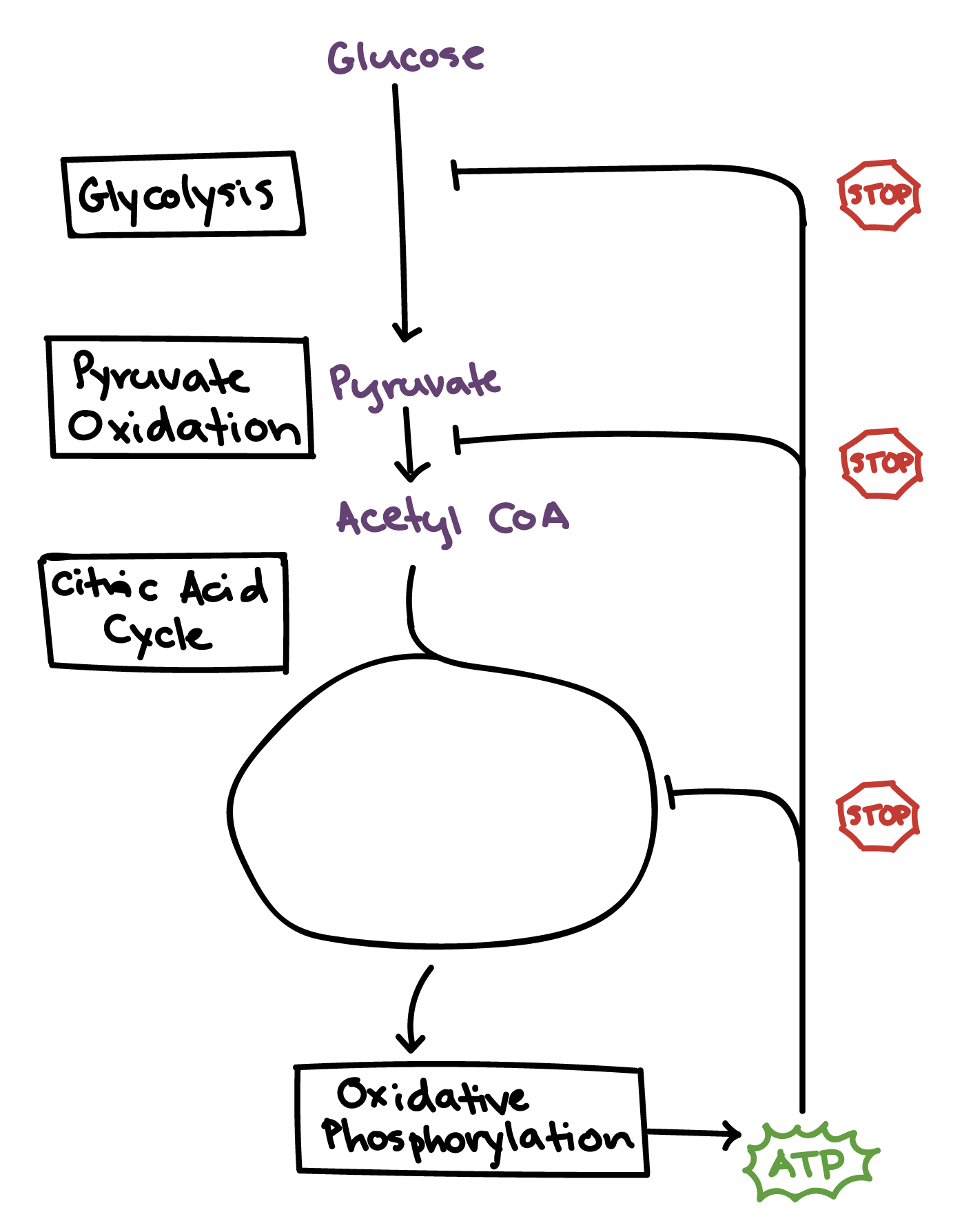
Regulation Of Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
Monomer amino acids.

. By increasing glucose uptake and decreasing cholesterol and lipid synthesis this regulation provides a. Others transport materials or help to fight disease. Allosteric regulation genetic and covalent modification and enzyme inhibition are all types of enzymatic regulation.
A source of nitrogen. Some proteins build tissues such as bone and muscle. These secretions come from a variety of glands which control various organs of the body.
NOT a primary source of energy common misconception Amino acid. Proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions in the cell without requiring high temperatures are antibodies. Reactions that are catalyzed by only one enzyme can go to equilibrium stalling the reaction.
The key functions are. Store and transmit genetic information Store and transmit genetic information is NOT a function of protein. An amino group -NH2 and a carboxyl group -COOH A polypeptide is formed when peptide bonds link amino acids together.
Proteins also act as biological catalysts in cells to control reactions Why does a body need protein. But the most rapid and general process that adjusts reaction rates operates through a. In cells they promote those reactions that are specific to the cells function.
Used to form bones muscle hair skin etc. 22 Votes The Endocrine system regulates the activities of the body by secreting complex chemical substances hormones into the blood stream. 55 248 Views.
Because enzymes ultimately determine which chemical reactions a cell can carry out and the rate at which they can proceed they are key to cell functionality. Control rate of chemical reactions through ENZYMES Bones and muscles transport things in and out of cells. AMPK affords both short- and long-term feedback control for cells by controlling the activity of numerous proteins through phosphorylation such as glucose transporters 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase and AcCoA carboxylase Hardie 2011.
Control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Can a cell turn off an enzyme. Move substances into or out of cells C.
Reactions that are catalyzed by only one enzyme can go to equilibrium stalling the reaction. Transport things in and out of cells. Specific enzymes catalyze each cellular reaction.
1 they control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes 2 form important cellular structures 3 transport substances into or out of cells or help fight disease What relationship exists between an enzyme and a catalyst. In this process all molecules follow the synthesis process to make bigger molecules. Enzymes can be inhibited in three ways.
In humans the frequency of cell turnover ranges from a few hours in early embryonic development to an average of two to five days for epithelial cells and to an entire human lifetime spent in G 0 by specialized cells such as cortical neurons or cardiac muscle cells. In contrast if two different enzymes each specific for a given direction are necessary for a reversible reaction the opportunity to control the rate of the reaction increases and equilibrium is. Proteins control the rate of chemical reactions enzymes and regulate cell processes within.
In contrast if two different enzymes each specific for a given direction are necessary for a reversible reaction the opportunity to control the rate of the reaction increases and equilibrium is. The main role of enzymes during the respiration reaction is to assist in transferring electrons from one molecule to another. Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes.
Amino Acid Compounds with two ends. Enzymes lower the activation energies of chemical reactions. A protein can control the rate of reaction and regulate the cell processes and from crucial cellular structures or transport substances out or into cells to help battle a disease.
All catalysts are enzymes. Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products. Control the rate of reactions B.
A second method that is commonly used by eucaryotic cells to regulate a proteins function is the covalent addition of a phosphate group to one of its amino acid. Identify three major roles of proteins. Help to fight disease D.
Competitive inhibition non-competitive inhibition or uncompetitive inhibition. How do enzymes regulate cellular reactions. Monomer of proteins polypeptides Peptide bond.
The rates of reactions in cells are rapid because of the effectiveness of enzyme. In the process of catabolism the larger molecules break into smaller molecules. What are three ways to control enzymes.
Enzymes are proteins that act as a biological catalyst Natures catalyst. Control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. The length of the cell cycle is highly variable even within the cells of a single organism.
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze or affect the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being altered in the process. All chemical reactions inside the living cell need a catalyst that can help in increasing the rate of the chemical reaction.

Regulation Of Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy


Comments
Post a Comment